When power outages strike unexpectedly, businesses and homeowners alike face the harsh reality of disrupted operations, spoiled food, and compromised security systems. In these critical moments, reliable backup power becomes essential for maintaining continuity and protecting valuable assets. Among the various power generation options available today, diesel generators have emerged as the undisputed champions of emergency power backup, offering unmatched reliability, fuel efficiency, and robust performance that keeps essential systems running when the grid fails.
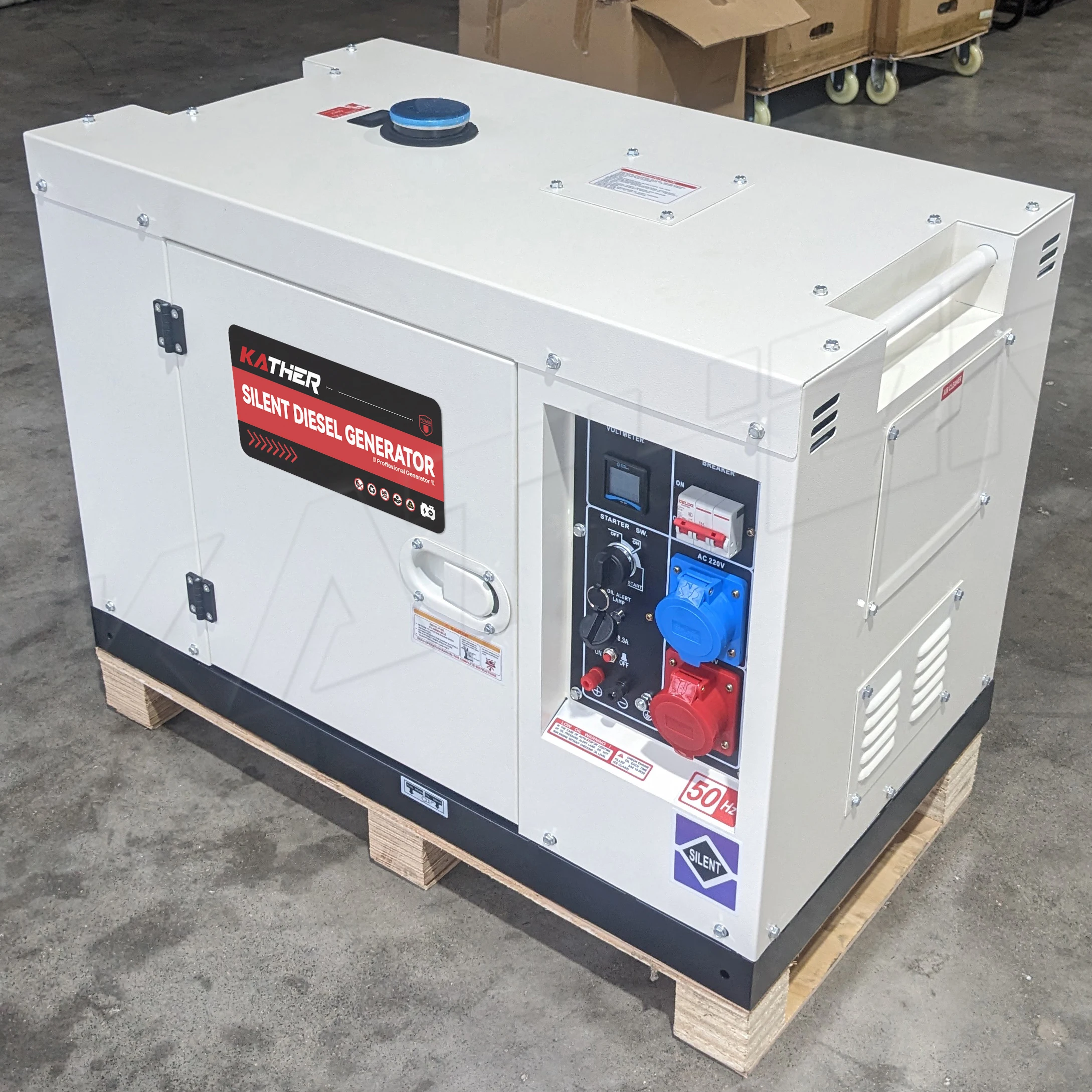

The superiority of diesel-powered backup systems extends far beyond mere convenience, encompassing critical factors such as operational costs, environmental considerations, and long-term durability. These powerhouse machines have been the backbone of emergency power infrastructure for decades, serving hospitals, data centers, manufacturing facilities, and residential complexes worldwide. Understanding why these units dominate the emergency power market requires examining their fundamental advantages and real-world applications.
Unmatched Reliability and Durability
Proven Track Record in Critical Applications
The reliability of diesel generators in emergency situations stems from their robust mechanical design and proven performance history across diverse industries. Hospitals rely on these units to maintain life-support systems during power outages, while data centers depend on them to prevent catastrophic server failures and data loss. The consistent performance of these systems under extreme conditions has established them as the gold standard for mission-critical applications.
Manufacturing facilities and industrial complexes have witnessed the exceptional reliability of diesel-powered backup systems during natural disasters, equipment failures, and grid instabilities. These units consistently deliver stable power output regardless of external weather conditions, making them indispensable for operations that cannot afford downtime. The mechanical simplicity of diesel engines, combined with fewer electronic components compared to alternative technologies, contributes significantly to their operational reliability.
Superior Engine Longevity and Maintenance Cycles
The inherent durability of diesel engines translates directly into extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements for backup power systems. Unlike gasoline engines that require frequent tune-ups and component replacements, diesel engines are engineered for heavy-duty operation with maintenance intervals often exceeding thousands of operating hours. This characteristic makes them particularly valuable for facilities requiring dependable standby power over extended periods.
The robust construction of diesel engines allows them to withstand the thermal and mechanical stresses associated with frequent start-stop cycles common in emergency power applications. Professional maintenance teams appreciate the straightforward diagnostic procedures and readily available replacement parts that keep these systems operational with minimal downtime. The ability to perform preventive maintenance without complex electronic diagnostics reduces both service costs and technical expertise requirements.
Superior Fuel Efficiency and Economic Advantages
Exceptional Energy Density and Consumption Rates
The outstanding fuel efficiency of diesel generators provides significant operational cost advantages compared to gasoline or natural gas alternatives. Diesel fuel contains approximately 15% more energy per gallon than gasoline, allowing these units to generate more electrical power from each unit of fuel consumed. This enhanced energy density becomes particularly valuable during extended power outages when fuel conservation directly impacts operational sustainability.
Industrial facilities operating large backup power systems benefit tremendously from the reduced fuel consumption rates of diesel engines. The efficiency gains become more pronounced as power demands increase, making diesel technology the preferred choice for facilities requiring substantial backup capacity. Fleet managers and facility operators consistently report lower fuel costs when comparing diesel-powered units to equivalent gasoline or propane systems over extended operational periods.
Long-Term Storage Capabilities and Fuel Stability
The superior storage characteristics of diesel fuel provide distinct advantages for emergency preparedness planning and long-term backup power strategies. Unlike gasoline, which deteriorates rapidly and requires frequent replacement, diesel fuel maintains its combustive properties for extended periods with proper storage conditions and minimal additive treatment. This stability allows facility managers to maintain substantial fuel reserves without concerns about degradation affecting generator performance during critical events.
Emergency preparedness protocols benefit significantly from the extended shelf life of diesel fuel, enabling organizations to maintain strategic fuel reserves that remain viable for months or even years. The reduced frequency of fuel replacement cycles translates into lower administrative costs and simplified inventory management procedures. Additionally, the lower volatility of diesel fuel reduces fire hazards and simplifies storage facility requirements compared to gasoline-based systems.
Robust Performance Under Extreme Conditions
Temperature Tolerance and Environmental Adaptability
The exceptional temperature tolerance of diesel engines enables reliable operation across diverse climatic conditions, from arctic environments to tropical regions with extreme heat and humidity. These units maintain consistent power output and starting reliability in temperatures ranging from sub-zero conditions to exceeding 120 degrees Fahrenheit, making them suitable for deployment in virtually any geographic location. The ability to function reliably in extreme weather conditions proves invaluable during natural disasters when backup power becomes most critical.
Cold weather performance represents a particular strength of modern diesel technology, with advanced glow plug systems and fuel heaters enabling reliable starts even in harsh winter conditions. Hurricane-prone regions rely heavily on these systems because they continue operating effectively despite high winds, driving rain, and temperature fluctuations that accompany severe weather events. The environmental adaptability of diesel engines reduces the need for specialized climate control systems, simplifying installation and reducing overall system costs.
Load Handling Capabilities and Power Quality
The superior load handling characteristics of diesel engines provide stable power delivery across varying electrical demands, making them ideal for applications with fluctuating power requirements. These units maintain consistent voltage and frequency regulation even when subjected to sudden load changes, protecting sensitive electronic equipment from power quality issues that could cause expensive damage or data corruption. The ability to handle both resistive and inductive loads effectively makes them versatile solutions for diverse backup power applications.
Industrial facilities appreciate the quick response times and load acceptance capabilities of diesel-powered systems when critical equipment comes online during power restoration sequences. The inherent torque characteristics of diesel engines enable rapid acceleration to full load without compromising power quality or system stability. This performance advantage becomes particularly important in applications where power interruption duration must be minimized to prevent process disruption or equipment damage.
Cost-Effectiveness and Return on Investment
Initial Investment Considerations and Value Proposition
While the initial purchase price of diesel generators may exceed that of gasoline alternatives, the total cost of ownership analysis consistently favors diesel technology for serious backup power applications. The extended service life, reduced maintenance requirements, and superior fuel efficiency combine to deliver substantial cost savings over the operational lifetime of these systems. Financial analyses conducted by facility managers and procurement professionals repeatedly demonstrate the superior return on investment provided by diesel-powered backup systems.
The value proposition becomes even more compelling when considering the reduced insurance premiums and business continuity benefits associated with reliable backup power systems. Many commercial insurance policies offer significant discounts for facilities equipped with proven emergency power systems, partially offsetting the initial investment costs. The ability to maintain operations during power outages prevents revenue losses that can quickly exceed the entire cost of a backup power system.
Maintenance Cost Advantages and Service Intervals
The extended maintenance intervals and lower service costs associated with diesel engines provide ongoing operational advantages that accumulate substantial savings over time. Professional maintenance contracts for these systems typically cost significantly less than equivalent services for gasoline or natural gas units, reflecting the reduced complexity and higher reliability of diesel technology. The availability of standardized maintenance procedures and widespread service network coverage further reduces operational costs and minimizes system downtime.
Component replacement costs remain reasonable due to the mature technology and competitive aftermarket parts availability for diesel engines. The standardization of diesel engine components across multiple manufacturers enables cost-effective sourcing of replacement parts and reduces inventory requirements for maintenance departments. Long-term operating cost projections consistently demonstrate the economic advantages of diesel technology for facilities requiring dependable backup power systems.
Environmental Considerations and Modern Efficiency
Emission Control Technology and Regulatory Compliance
Modern diesel generators incorporate advanced emission control technologies that significantly reduce environmental impact while maintaining the performance advantages that have made them the preferred choice for emergency power applications. Tier 4 emission standards compliance ensures that contemporary units meet stringent environmental regulations without compromising reliability or operational efficiency. These technological advances have addressed historical concerns about diesel emissions while preserving the fundamental advantages of diesel technology.
The implementation of selective catalytic reduction systems, diesel particulate filters, and advanced fuel injection technologies has dramatically improved the environmental profile of modern diesel generators. These systems operate at significantly higher efficiency levels than older units while producing substantially lower emissions per kilowatt-hour of electrical output. Regulatory compliance with EPA standards ensures that these units can be deployed in environmentally sensitive areas without compromising air quality objectives.
Carbon Footprint and Efficiency Comparisons
Comprehensive lifecycle analyses demonstrate that the superior fuel efficiency of diesel generators often results in lower overall carbon emissions compared to less efficient alternatives, particularly when considering the entire fuel supply chain and transportation impacts. The higher energy content of diesel fuel, combined with the superior thermal efficiency of diesel engines, produces more electrical energy per unit of carbon dioxide released. This efficiency advantage becomes more pronounced during extended power outages when fuel consumption directly impacts environmental impact.
The reduced frequency of refueling operations required by diesel systems minimizes transportation-related emissions and fuel delivery logistics. Emergency response scenarios particularly benefit from this characteristic, as fuel supply chains may be disrupted during natural disasters or other emergency conditions. The ability to operate for extended periods between refueling cycles reduces the environmental impact associated with fuel transportation and handling operations.
FAQ
How long can diesel generators run continuously during emergencies
Most modern diesel generators can operate continuously for 24 to 48 hours between refueling cycles, depending on load conditions and fuel tank capacity. Industrial-grade units with large fuel tanks can extend this runtime to several days or even weeks with proper fuel supply arrangements. The continuous duty rating of diesel engines allows for extended operation without the cooling periods required by some gasoline alternatives, making them ideal for prolonged power outages.
What maintenance is required to keep diesel generators reliable
Regular maintenance for diesel generators includes periodic oil changes, fuel filter replacements, cooling system inspections, and battery maintenance, typically performed every 250-500 operating hours or annually for standby units. Monthly exercise runs help maintain engine readiness and identify potential issues before they become critical. Professional maintenance contracts ensure compliance with manufacturer warranties and help maximize system reliability through preventive care protocols.
Are diesel generators suitable for residential backup power applications
Yes, diesel generators are excellent choices for residential backup power, particularly for homes with substantial electrical loads or those in areas prone to extended power outages. Modern residential diesel units feature sound attenuation technology that minimizes noise concerns while providing reliable whole-house backup power. The fuel efficiency and extended runtime capabilities make them particularly valuable for homes requiring reliable backup power for medical equipment or home-based businesses.
How do diesel generators compare to natural gas backup systems
Diesel generators typically offer superior portability, fuel storage independence, and performance reliability compared to natural gas systems, though natural gas units may have advantages in urban areas with reliable gas infrastructure. Diesel systems excel in remote locations or areas where natural gas service may be interrupted during emergencies. The choice between technologies often depends on specific site conditions, fuel availability, and local utility infrastructure reliability.