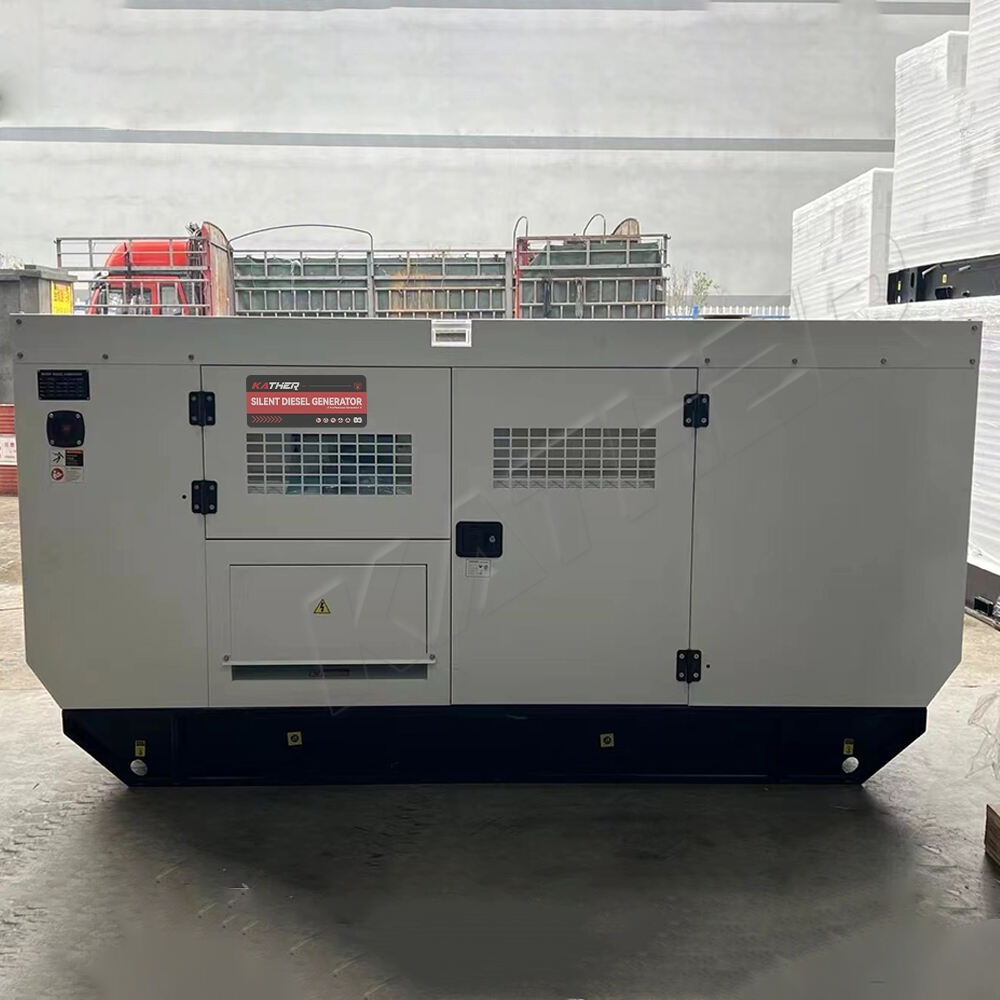
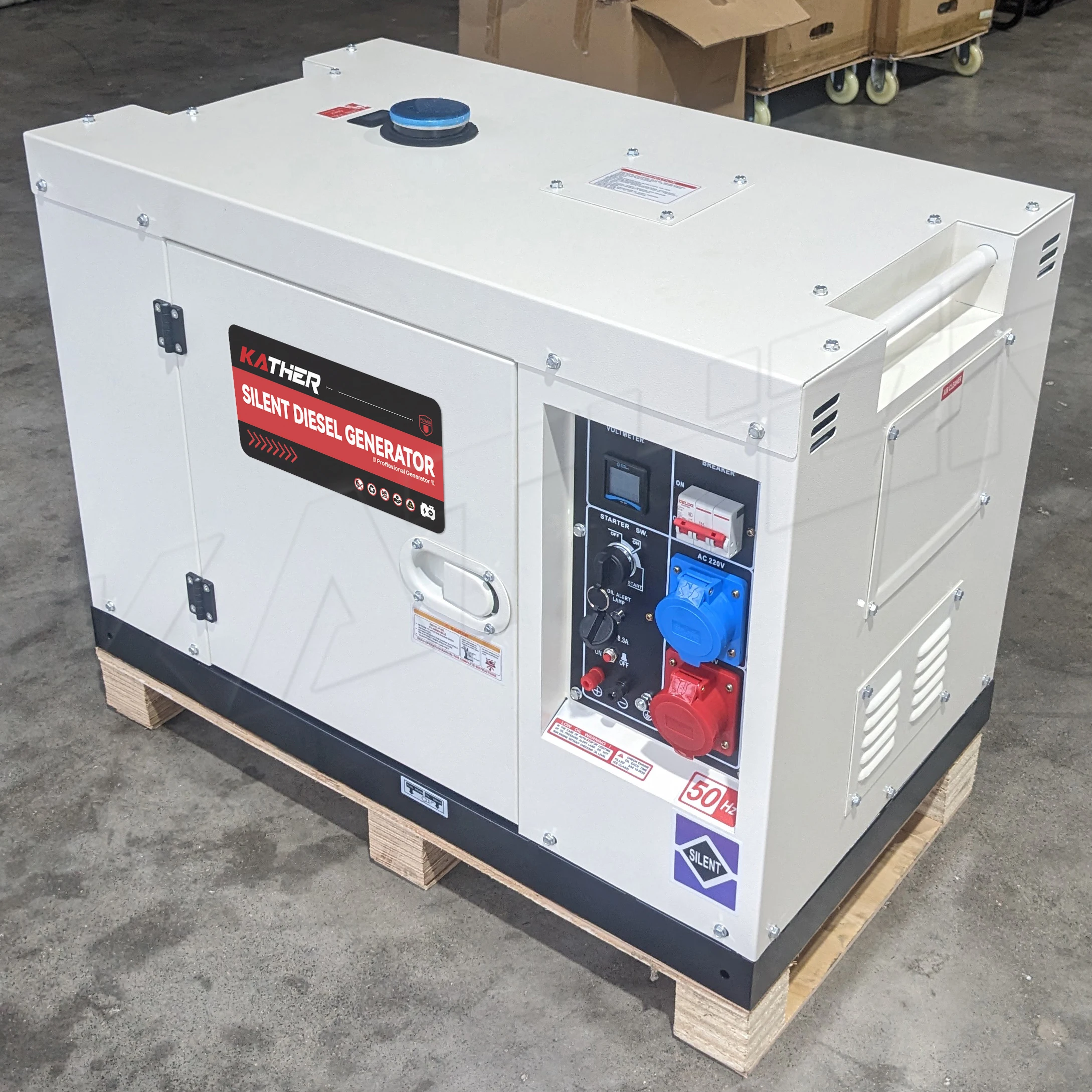
Proper maintenance is the cornerstone of maximizing the operational lifespan and efficiency of diesel generators. These robust power solutions serve as critical backup systems across industries, from manufacturing facilities to data centers, where uninterrupted power supply is non-negotiable. Understanding the fundamental maintenance practices can significantly extend equipment life, reduce unexpected failures, and ensure optimal performance when power is needed most. Regular maintenance not only protects your investment but also maintains the reliability that makes diesel generators indispensable for mission-critical operations.

Essential Engine Maintenance Procedures
Oil System Management and Filtration
The engine oil system represents the lifeblood of any generator engine, requiring meticulous attention to maintain optimal lubrication and cooling properties. Regular oil changes should follow manufacturer specifications, typically ranging from 100 to 500 operating hours depending on load conditions and environmental factors. Quality engine oil reduces friction between moving components, prevents excessive wear, and helps dissipate heat generated during operation. Oil filter replacement must accompany every oil change to ensure contaminants do not circulate through the engine system.
Monitoring oil levels between service intervals prevents catastrophic engine damage from insufficient lubrication. Check oil quality by examining color, consistency, and the presence of metal particles or contaminants. Dark, thick oil or oil containing debris indicates the need for immediate replacement. Maintain detailed records of oil changes, including dates, operating hours, and oil quality observations to establish maintenance patterns and predict future service requirements.
Air Filter System Optimization
Clean air intake is fundamental for efficient combustion and engine longevity in generator applications. Air filters prevent dust, debris, and contaminants from entering the combustion chamber, where they could cause excessive wear or damage to internal components. Inspect air filters monthly or after every 50 operating hours, depending on environmental conditions. Dusty or industrial environments require more frequent filter inspection and replacement to maintain adequate airflow.
Replace air filters when they appear visibly dirty or when airflow restriction becomes apparent through reduced engine performance. A clogged air filter forces the engine to work harder, reducing efficiency and potentially causing overheating. Some generator systems feature multiple-stage filtration with pre-filters and main filters that require different replacement intervals. Understanding your specific filtration system ensures comprehensive protection against airborne contaminants that could compromise engine performance.
Fuel System Maintenance Strategies
Fuel Quality and Storage Management
Maintaining high-quality fuel is crucial for reliable operation and extended service life of generator equipment. Diesel fuel degrades over time, forming sediments and developing microbial growth that can clog filters and injection systems. Use fuel stabilizers when storing generators for extended periods, and implement fuel rotation schedules to prevent deterioration. Fresh fuel ensures optimal combustion efficiency and reduces the risk of fuel system complications during critical operation periods.
Water contamination represents one of the most common fuel-related issues affecting generator performance. Install water separators and drain them regularly to prevent water from reaching the engine. Check fuel tanks monthly for signs of water accumulation, rust, or sediment buildup. Clean fuel tanks annually or when contamination is detected to maintain fuel system integrity. Proper fuel storage in clean, sealed containers with appropriate additives extends fuel life and protects sensitive injection components.
Fuel Filter and Injection System Care
The fuel filtration system requires regular attention to prevent contaminants from reaching precision injection components. Primary and secondary fuel filters should be replaced according to manufacturer schedules, typically every 250 to 500 operating hours. Clogged fuel filters restrict fuel flow, causing poor engine performance, increased emissions, and potential injection system damage. Monitor fuel pressure gauges when available to identify filtration issues before they affect engine operation.
Fuel injection systems demand clean fuel and proper pressure to function effectively. Contaminated fuel or worn filters can damage expensive injection components, requiring costly repairs and extended downtime. Professional injection system cleaning and calibration should be performed annually or as recommended by the manufacturer. This preventive maintenance ensures optimal fuel delivery, maintains emissions compliance, and preserves the precision required for efficient combustion in modern diesel generators.
Cooling System Maintenance Excellence
Radiator and Coolant System Care
The cooling system prevents engine overheating and maintains optimal operating temperatures under varying load conditions. Regular coolant level checks ensure adequate heat transfer capacity and prevent air pockets that could cause localized overheating. Use only manufacturer-recommended coolant types and mixing ratios to maintain proper corrosion protection and heat transfer properties. Coolant replacement intervals typically range from 1,000 to 3,000 operating hours, depending on coolant type and operating conditions.
Radiator cleanliness directly impacts cooling efficiency and overall system performance. Remove debris, leaves, and dirt from radiator fins monthly or more frequently in dusty environments. Use compressed air or water washing to clean radiator surfaces, working from the inside out to avoid pushing debris deeper into the fins. Inspect radiator hoses for signs of wear, cracking, or swelling that could indicate impending failure. Replace worn hoses proactively to prevent coolant leaks that could lead to engine overheating.
Thermostat and Water Pump Functionality
The thermostat regulates engine operating temperature by controlling coolant flow through the radiator system. A malfunctioning thermostat can cause overheating or prevent the engine from reaching optimal operating temperature, both of which reduce efficiency and increase wear. Test thermostat operation annually by monitoring engine temperature during warm-up cycles. Replace thermostats that fail to open at the specified temperature or show signs of corrosion or mechanical damage.
Water pump maintenance involves monitoring for leaks, unusual noises, or signs of bearing wear that indicate impending failure. The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator system, making it critical for temperature control. Inspect water pump seals regularly for signs of coolant leakage, which often appears as dried coolant residue around the pump housing. Replace water pumps showing signs of wear before failure occurs, as pump failure can cause severe engine damage from overheating.
Electrical System and Battery Maintenance
Battery Care and Testing Protocols
Generator batteries provide the electrical power necessary for engine starting and control system operation. Regular battery maintenance includes checking electrolyte levels in serviceable batteries, cleaning terminals to prevent corrosion, and testing battery capacity under load conditions. Maintain electrolyte levels using distilled water only, and ensure terminals are tight and free from corrosion buildup that could prevent reliable starting.
Battery testing should include both voltage and load testing to verify starting capability. Voltage testing alone may not reveal batteries that cannot deliver adequate current under starting loads. Perform load testing annually or when starting problems occur to identify weak batteries before they fail completely. Replace batteries that fail load tests or show signs of physical damage, swelling, or electrolyte leakage to maintain reliable starting capability.
Alternator and Charging System Inspection
The charging system maintains battery charge during operation and provides electrical power for generator control systems. Monitor charging system output regularly to ensure proper battery charging and electrical system operation. Charging voltage should remain within manufacturer specifications during operation, typically between 13.5 and 14.5 volts for 12-volt systems. Low charging voltage indicates potential alternator problems that require immediate attention.
Inspect alternator belts for proper tension, wear, and alignment to ensure reliable charging system operation. Loose or worn belts can slip under load, reducing charging output and potentially causing alternator damage. Check belt tension monthly and adjust according to manufacturer specifications. Replace belts showing signs of cracking, fraying, or excessive wear before they fail and cause charging system problems that could leave batteries discharged.
Scheduled Maintenance and Record Keeping
Preventive Maintenance Scheduling
Establishing a comprehensive preventive maintenance schedule based on operating hours and calendar time ensures all critical components receive proper attention. Create maintenance checklists for daily, weekly, monthly, and annual tasks to systematically address all generator systems. Daily checks should include fluid levels, battery condition, and visual inspections for leaks or damage. Weekly maintenance might include more detailed inspections of belts, hoses, and electrical connections.
Monthly maintenance tasks typically involve filter inspections, coolant system checks, and fuel quality assessment. Annual maintenance includes major service items like oil changes, filter replacements, and comprehensive system testing. Adjust maintenance intervals based on operating conditions, with more frequent service required for generators operating in harsh environments or under heavy loads. Consistent adherence to scheduled maintenance prevents minor issues from developing into major problems.
Documentation and Performance Tracking
Detailed maintenance records provide valuable insights into generator performance trends and help predict future maintenance needs. Document all maintenance activities, including dates, operating hours, parts replaced, and observations about system condition. Track fuel consumption, oil consumption, and coolant usage to identify trends that might indicate developing problems. Regular performance monitoring helps optimize maintenance intervals and identifies components requiring more frequent attention.
Maintain warranty documentation and service records for potential warranty claims and resale value preservation. Comprehensive maintenance records demonstrate proper care and can significantly impact generator value during equipment transfers or sales. Use maintenance management software or detailed logbooks to ensure consistent record keeping and easy access to historical maintenance data for troubleshooting and planning purposes.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I change the oil in my generator
Oil change intervals depend on several factors including generator load, operating environment, and manufacturer recommendations. Typically, oil should be changed every 100-200 hours of operation for standby generators and every 50-100 hours for generators operating under heavy loads or in dusty conditions. Always check your specific manufacturer guidelines and consider more frequent changes if the oil appears contaminated or if operating conditions are particularly harsh.
What are the signs that my generator needs immediate maintenance
Warning signs requiring immediate attention include unusual noises, excessive smoke, fluid leaks, difficulty starting, irregular operation, or warning lights on the control panel. Other indicators include low oil pressure, high engine temperature, unusual vibrations, or fuel consumption changes. Address any of these symptoms immediately to prevent minor issues from becoming major repairs that could result in extended downtime.
Can I perform generator maintenance myself or should I hire professionals
Basic maintenance tasks like checking fluid levels, cleaning air filters, and visual inspections can typically be performed by trained facility personnel. However, major maintenance involving engine internals, fuel injection systems, or electrical components should be performed by qualified technicians. Professional service ensures proper procedures, genuine parts, and warranty compliance while reducing the risk of damage from incorrect maintenance practices.
How long can a well-maintained generator last
With proper maintenance, quality generators can operate reliably for 15-30 years or more, depending on usage patterns and environmental conditions. Standby generators that operate infrequently may last decades with proper care, while generators under constant use may require major overhauls every 10-15 years. The key to longevity is consistent preventive maintenance, quality parts, and prompt attention to any developing issues before they cause major damage.