Moderné poľnohospodárstvo vyžaduje presnosť a efektivitu pri príprave pôdy, čo robí výber vhodných modelov kultivátorov rozhodujúcim pre úspešný chod poľnohospodárskych podnikov. Tieto univerzálne stroje zmenili spôsob, akým poľnohospodári pristupujú k obrobě pôdy, riadeniu burín a príprave rýh na plodiny v rámci rozmanitých poľnohospodárskych podmienok. Porozumenie rôznym modelom kultivátorov dostupným na dnešnom trhu umožňuje poľnohospodárom robiť informované rozhodnutia, ktoré priamo ovplyvňujú ich prevádzkovú efektivitu a výnosy plodín.
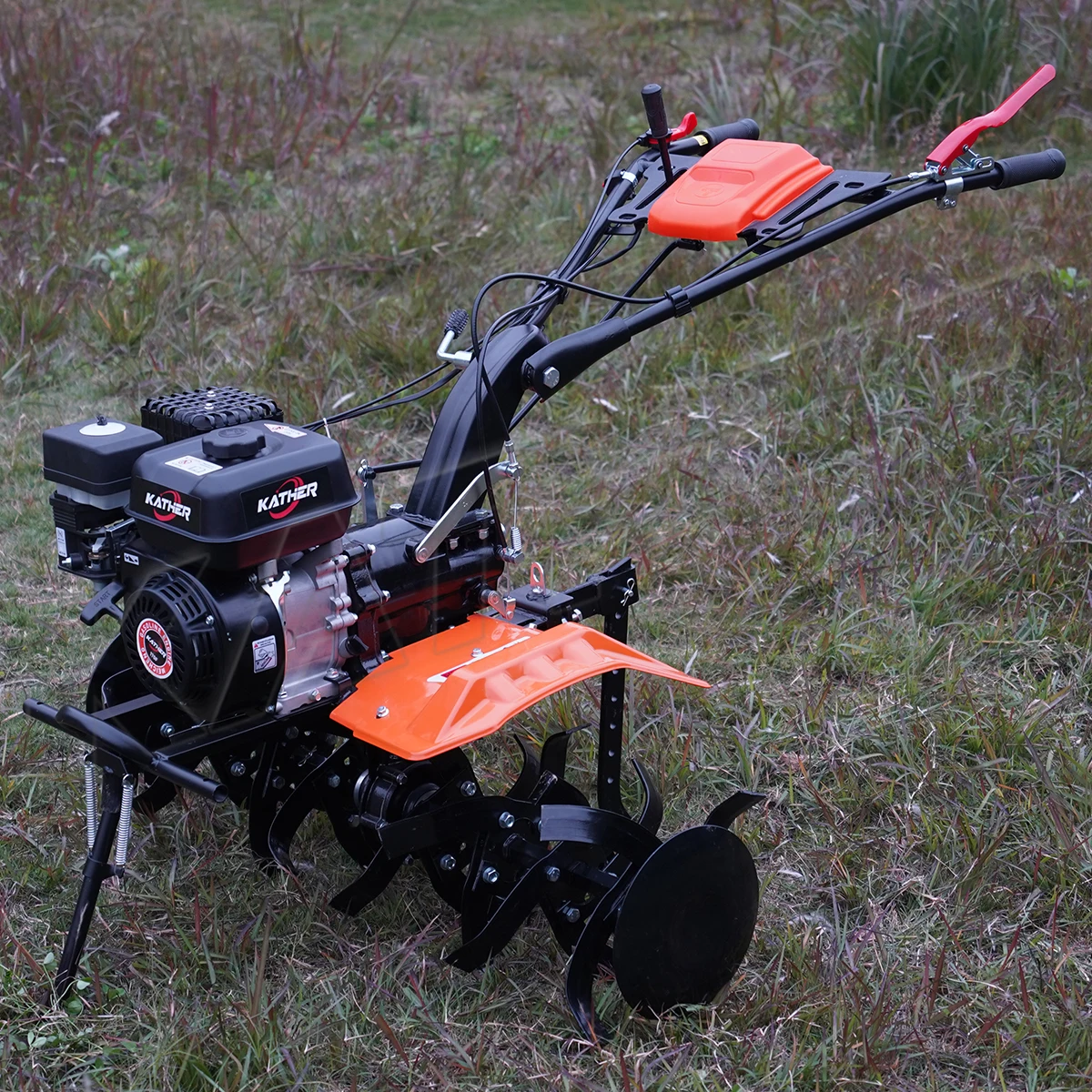

Trh poľnohospodárskych strojov ponúka širokú škálu modelov kultivátorov určených na splnenie konkrétnych požiadaviek poľnohospodárstva. Od kompaktných záhradných kultivátorov vhodných pre malé prevádzky až po výkonné polné kultivátory schopné obrábať rozsiahle plochy – každý model plní odlišný účel v procese pestovania. Profesionálni poľnohospodári čoraz viac uznávajú, že investícia do správnej kultivačnej technológie výrazne zníži pracovné náklady, zároveň zlepší štruktúru pôdy a podmienky pre vzchádzanie plodín.
Súčasné modely kultivátorov zahŕňajú pokročilé inžinierske vlastnosti, ktoré zvyšujú výkon, trvanlivosť a bezpečnosť používateľa. Tieto inovácie riešia tradičné problémy pri obnaše, ako je zhutnenie pôdy, nerovnomerná hĺbka orbty a nadmerná spotreba paliva. Keďže poľnohospodárske postupy sa posúvajú smerom k udržateľným metódam pestovania, moderné kultivátory hrajú nevyhnutnú úlohu pri uplatňovaní techník šetrnej obrábania pôdy, ktoré zachovávajú zdravie pôdy a minimalizujú dopad na životné prostredie.
Základné vlastnosti moderných modelov kultivátorov
Výkon motora a technické parametre
Srdcom každého efektívneho kultivátora sú vlastnosti jeho motora, ktoré určujú schopnosť stroja zvládať rôzne typy pôdy a úlohy pri obpracovaní pôdy. Vysoko kvalitné modely kultivátorov sú vybavené motormi od ľahkých dvojtaktných jednotiek s výkonom 1–3 koňa pre malé záhrady až po výkonné štvortaktné motory s výkonom 15–25 koňa pre komerčné použitie. Tieto výkonové parametre priamo súvisia s možnosťou kultivátora preniknúť do zhutnenej pôdy, udržať konštantnú hĺbku barienia a efektívne pracovať po dlhšie obdobie.
Technológia motora v moderných kultivátoroch zdôrazňuje úspornosť paliva a zníženie emisií bez poškodenia výkonu. Pokročilé systémy karburátorov a elektronické zapalovacie moduly zabezpečujú spoľahlivé štartovanie za rôznych poveternostných podmienok, pričom optimalizujú spotrebu paliva. Modely kultivátorov profesionálnej triedy často zahŕňajú funkcie, ako sú automatické systémy škrtiacej klapky, mechanizmy na štartovanie ťahom a motory s tlmením vibrácií, ktoré zvyšujú pohodlie obsluhy a znižujú nároky na údržbu.
Prevodové systémy v súčasných modeloch kultivátorov ponúkajú viacnásobné nastavenie rýchlosti a spätný chod, čo umožňuje obsluhe upravovať pracovné rýchlosti podľa stavu pôdy a cieľov orby. Rýchlosť dopredu sa zvyčajne pohybuje od 1 do 4 mph, pričom niektoré modely ponúkajú nekonečne premenlivé riadenie rýchlosti prostredníctvom hydrostatických prevodoviek. Táto flexibilita umožňuje presné riadenie hĺbky obpracovania pôdy a intenzity miešania pôdy, čo vedie k vynikajúcej príprave semenísk a efektívnej kontrole burín.
Konfigurácia kolíkov a systémy zasahovania do pôdy
Usporiadanie a konštrukcia kolíkov významne ovplyvňujú účinnosť kultivátora pri rozrušovaní hrudiek pôdy, začleňovaní organickej hmoty a odstraňovaní burín. Vysokovýkonné modely kultivátorov vlastnosť tvrdené ocele s hrotmi usporiadanými do špecifických vzorov, ktoré maximalizujú účinnosť zásahu do pôdy a zároveň minimalizujú požiadavky na výkon. Najbežnejšie konfigurácie zahŕňajú priame hrady na prvotné rozrušenie pôdy, zakrivené hrady na miešanie a drvenie, a špecializované hrady na odstraňovanie burín určené pre riadenie vegetácie.
Nastaviteľná kontrola hĺbky hrádov umožňuje operátorom prispôsobiť intenzitu orby podľa požiadaviek plodín a stavu pôdy. Profesionálne modely orbárov obsahujú hydraulické alebo mechanické systémy nastavenia hĺbky, ktoré udržiavajú konzistentnú pracovnú hĺbku aj na nerovnom teréne. Niektoré pokročilé modely sú vybavené individuálnymi systémami odpruženia hrádov, ktoré sa automaticky prispôsobujú reliéfu povrchu, čím zabezpečujú rovnomernú prípravu pôdy a predchádzajú poškodeniu podzemných zavlažovacích systémov alebo pozostatkov po úrodách.
Vzdialenosť medzi hrotmi ovplyvňuje efektivitu orby a charakteristiky toku pôdy. Širšia vzdialenosť medzi hrotmi znižuje požiadavky na výkon a umožňuje lepší tok zvyškov rastlín pri konzervačnej orbe, zatiaľ čo menšia vzdialenosť zabezpečuje intenzívnejšie premiešanie pôdy a kontrolu burín. Vysoko kvalitné modely kultivátorov ponúkajú vymeniteľné súpravy hrotov, ktoré je možné rýchlo prenastaviť pre rôzne orby, čím sa maximalizuje univerzálnosť stroja pri rôznorodých poľnohospodárskych operáciách.
Kompaktné modely záhradných kultivátorov pre malé prevádzky
Ľahké elektrické a batériou poháňané varianty
Modely elektrických kultivátorov získali veľkú popularitu medzi mestskými záhradníkmi a drobnými poľnohospodármi vďaka tichému chodu, nulovým emisiám a minimálnym nárokom na údržbu. Tieto modely zvyčajne disponujú elektrickými motormi s prúdom od 8 do 15 ampérov, čo poskytuje dostatočný výkon na obpracovanie záhradných lôžok, kvetinových okrajov a malých zeleninových pozemkov. Ľahký dizajn elektrických kultivátorov, ktoré zvyčajne vážia medzi 15 a 30 librami, umožňuje jednoduchú ovládateľnosť v obmedzených priestoroch a znižuje únavu obsluhy pri dlhšom používaní.
Modely kultivátorov s batériovým pohonom ponúkajú výhodu prevádzky bez kábla a zároveň zachovávajú ekologickosť. Pokročilé systémy batérií s iónmi lítia umožňujú nepretržitú prevádzku po dobu 30 až 60 minút na jedno nabitie, čo je postačujúce pre väčšinu úloh v záhradách rodinných domov. Tieto modely sú vybavené funkciou rýchleho nabíjania a vymeniteľnými batériovými balíkmi, ktoré predlžujú pracovný čas pri rozsiahlejších projektoch. Vzhľadom na to, že nie je potrebné miešať palivo a nevytvárajú sa emisie, sú batériové kultivátory obzvlášť vhodné pre ekologické záhradníctvo a použitie v skleníkoch v uzavretých priestoroch.
Moderné modely elektrických kultivátorov zahŕňajú ergonomické prvky, ako sú nastaviteľné rukoväte, podložené rukoväti a vyvážené rozloženie hmotnosti, ktoré zvyšujú pohodlie a kontrolu používateľa. Bezpečnostné funkcie zahŕňajú okamžité vypínacie prepínače, ochranné kryty okolo rotujúcich vidlík a systémy riadenia káblov, ktoré zabraňujú náhodnému odpojeniu počas prevádzky. Tieto kultivátory sa osvedčili pri príprave záhonov, začleňovaní kompostu a organických prísad a udržiavaní už zavedených záhradných plôch s minimálnym narušením pôdy.
Kompaktné kultivátory so spaľovacím motorom
Malé kultivátory so spaľovacími motormi zaberajú medzistupeň medzi elektrickými zariadeniami a plnohodnotnými poľnohospodárskymi strojmi a ponúkajú vyšší výkon a mobilitu pre stredne veľké pozemky a záhradnícke podniky. Tieto stroje sú zvyčajne vybavené motormi s výkonom 2–4 koňských síl, ktoré poskytujú dostatočný krútiaci moment na rozorané nové pôdy, obpracovanie už založených záhradných lôh a odstraňovanie burín z riadkových plodín. Nezávislá mobilita kultivátorov so spaľovacím motorom odstraňuje obmedzenia dosahu káblových elektrických modelov a zároveň ponúka vyššiu hustotu výkonu v porovnaní s batériami napájanými alternatívami.
Šírka obrábania kompaktných benzínových kultivátorov sa pohybuje od 6 do 16 palcov, čo ich robí ideálnymi na prácu medzi už založenými rastlinami a v úzkych záhradných radách. Mnohé modely ponúkajú nastaviteľnú šírku obrábania prostredníctvom odstrániteľných vonkajších hrábľov, čo umožňuje prevádzkovateľom prispôsobiť pracovnú šírku konkrétnym aplikáciám. Hĺbka orby sa zvyčajne pohybuje od 2 do 8 palcov, čo je postačujúce pre väčšinu úloh pripravy záhradnej pôdy a kontroly plevelu, pričom sa vyhýba poškodeniu povrchových koreňových sústav.
Hospodárnosť paliva a jednoduchá údržba predstavujú kľúčové výhody moderných kompaktných modelov kultivátorov. Štvordobé motory eliminujú potrebu miešania paliva a zároveň ponúkajú lepšiu spotrebu paliva a znížené emisie v porovnaní so staršími dvojdobými konštrukciami. Údržbové prvky bez nástrojov, ako napríklad ľahko prístupné vzduchové filtre, systémy rýchleho odčerpania oleja a zjednodušená výmena sviečok, znížia technické znalosti potrebné na bežnú údržbu, čo tieto kultivátory sprístupňuje aj začiatočníkom.
Modely kultivátorov strednej triedy pre komerčné záhrady
Profesionálne kultivátory s posunom za sebou
Profesionálne modely kultivátorov s posunom za sebou vyhovujú potrebám záhradkárov na trhu, záhradkárskych dodávateľov a malých komerčných poľnohospodárskych prevádzok, ktoré potrebujú väčšiu výkonnosť a odolnosť, než čo dokážu poskytnúť domáce jednotky. Tieto stroje zvyčajne disponujú motormi s výkonom 5–10 koňských síl spojenými s robustnými prevodovými systémami, ktoré zabezpečujú stály výkon za náročných prevádzkových podmienok. Zvýšený výkon umožňuje týmto kultivátorom efektívne pracovať s ťažšími pôdami, začleňovať väčšie množstvá organickej hmoty a udržiavať produktivitu počas dlhších pracovných období.
Kvalita výstavby komerčných modelov kultivátorov zdôrazňuje trvanlivosť a spoľahlivosť prostredníctvom použitia zosilnených rámov, tesnených ložísk a odolných pohonných komponentov. Puzdrá prevodoviek z liatiny a bronzové ložiská odolávajú opotrebovaniu v prachom znečistenom a nečistotami nasýtenom prostredí, zatiaľ čo tesnené pohonové reťaze eliminujú potrebu častého mazania a nastavovania. Tieto konštrukčné prvky prispievajú k predĺženej životnosti a zníženým prevádzkovým nákladom, čo sú kritické faktory v komerčných aplikáciách, kde výpadok zariadenia priamo ovplyvňuje ziskovosť.
Prevádzková všestrannosť predstavuje ďalšiu kľúčovú výhodu profesionálnych modelov kultivátorov, pričom mnohé jednotky ponúkajú viacero možností príslušenstva, ktoré rozširujú ich funkčnosť nad rámec základného kultivovania. Bežným príslušenstvom patria radovicové pluhové súpravy na vytváranie riadkov pre výsadbu, aplikátory hnojív do radov a špecializované nástroje na kultiváciu buriny. Schopnosť rýchlo meniť príslušenstvo umožňuje prevádzkovateľom vykonávať viaceré poľné operácie jediným strojom, čím sa znížia náklady na vybavenie a zvyšuje sa prevádzková efektívnosť.
Samojazdné systémy kultivátorov
Modely samojezdných kultivátorov odstraňujú fyzické zaťaženie spôsobené tlačením ťažkého zariadenia a zároveň poskytujú vynikajúcu kontrolu a presnosť pri kultivačných operáciách. Tieto stroje sú vybavené nezávislými pohonom kolies, ktorý udržiava konštantnú rýchlosť jazdy dopredu bez ohľadu na odpor pôdy, čím zabezpečujú rovnomernú hĺbku kultivácie a intenzitu premiešania pôdy. Operátor ide za strojom, riadi smer a sleduje výkon, zatiaľ čo systém samojezdnosti zvláda fyzickú prácu pohybu cez náročné pôdne podmienky.
Pokročilé samojezdne kultivátory zahŕňajú prevodové systémy s premennou rýchlosťou, ktoré umožňujú presné prispôsobenie rýchlosti požiadavkám kultivácie. Pomalšie rýchlosti zabezpečujú intenzívne premiešavanie pôdy a kontrolu burín, zatiaľ čo vyššie rýchlosti umožňujú rýchle pokrytie veľkých plôch počas prvej fázy prípravy pôdy. Niektoré modely majú funkciu jazdy vzad, ktorá uľahčuje manévrovanie v obmedzených priestoroch a odchod späť od prekážok bez zdvihania alebo preusporiadania ťažkej strojnej jednotky.
Zvýšená stabilita a ovládanie, ktoré ponúkajú modely samojezdných kultivátorov, ich robia mimoriadne účinnými pri presných pracovných úlohách, ako je práca v blízkosti už vysadených plodín, manévrovanie okolo zavlažovacích potrubí a udržiavanie konštantnej hĺbky na svahovitom teréne. Protivyberačné systémy a ergonomicky usporiadané ovládacie prvky znižujú únavu obsluhy a zvyšujú presnosť počas dlhodobej prevádzky, čím prispievajú k vyššej produktivite a lepším výsledkom kultivácie.
Modely kultivátorov pre rozsiahle poľnohospodárske pestovanie
Systémy kultivátorov upevňované na traktory
Veľké poľnohospodárske prevádzky sa spoliehajú na modely kultivátorov upevňované na traktory, ktoré využívajú výkon a mobilitu poľnohospodárskych traktorov na dosiahnutie vysokokapacitnej prípravy a obpracovania pôdy. Tieto pracovné zariadenia sa pripájajú k trojbodovému zavesovaciemu systému traktora alebo sa ťahajú za ním a využívajú hydraulický výkon traktora a výkon odberu hnacej sily (PTO) na súčasné prevádzkovanie viacerých kultivačných ramien. Pracovná šírka sa pohybuje od 8 do 30 stôp, čo umožňuje rýchle pokrytie rozsiahlych výmer a zároveň zachováva konzistentnú kvalitu kultivácie po celej pracovnej šírke zariadenia.
Konštrukcia kultivátorov upravovaných pre traktory zdôrazňuje štrukturálnu pevnosť a prevádzkovú flexibilitu, aby vyhovovali náročným podmienkam veľkých poľnohospodárskych podnikov. Rám z vysokopevnej ocele odolný voči deformácii a únave materiálu odoláva silám vznikajúcim pri práci viacerých oracích nožov v náročných pôdnych podmienkach. Hydraulický systém regulácie hĺbky umožňuje presné nastavenie hĺbky obpracovania pôdy po celej pracovnej šírke náradia, čím zabezpečuje rovnomernú prípravu pôdy a optimálne podmienky pre sejacie lôžko.
Moderné modely kultivátorov na traktory zahŕňajú pokročilé funkcie, ako je automatická kontrola sekcií, kompatibilita so systémom GPS navigácie a nastavenie premenlivej hĺbky, ktoré optimalizujú efektivitu orby a znížia pracovnú záťaž operátora. Tieto technológie umožňujú presnú obrábotku okolo hraníc polí, automatické zdvihnutie nad vodné toky a prekážky a dokumentovanie činností pri orbote za účelom evidencie a dodržiavania predpisov. Integrácia technológií presnej poľnohospodárskej produkcie mení tradičnú obrábotku na proces riadený dátami, ktorý maximalizuje efektivitu a zároveň minimalizuje dopad na životné prostredie.
Špecializované kultivátory pre radové plodiny
Modely radových kultivátorov riešia špecifické potreby poľnohospodárov pestujúcich kukuricu, repku, bavlnu a iné plodiny, ktoré vyžadujú presnú úpravu pôdy medzi zasadenými radmi bez rušenia rastlín. Tieto špecializované stroje disponujú nastaviteľnou vzdialenosťou radov, ktorá umožňuje prispôsobenie rôznym usporiadaniam plodín, zvyčajne v rozmedzí od 15-palcových po 40-palcové vzdialenosti radov. Orné ramená sú presne umiestnené tak, aby upravovali pôdu medzi radmi plodín a zároveň zachovávali bezpečnú vzdialenosť od stoniek rastlín a ich koreňových zón.
Účinnosť radových kultivátorov závisí od presného nastavenia hĺbky a bočnej polohy vzhľadom na rady plodín. Moderné modely sú vybavené GPS navigačnými systémami a automatickým riadením, ktoré zabezpečujú presné umiestnenie pracovného zariadenia aj pri vyšších pracovných rýchlostiach. Táto technológia eliminuje odhadovanie a únavu obsluhy spojenú s manuálnym riadením a zároveň zabezpečuje konzistentnú kvalitu orby za rôznych podmienok poľa a terénnych zmien.
Účinnosť ochrany proti plevelu predstavuje hlavný cieľ orby medzi riadkami, ktorá vyžaduje špeciálne návrhy ramien a techniky orb, ktoré maximalizujú odstránenie plevelu a minimalizujú poškodenie plodín. Široké korenie podrezáva korene plevelu a súčasne odklápa voľnú pôdu smerom k riadkom plodín, čím zahrabáva malé plevely. Ramená s pružinovým nastavením sa automaticky prispôsobujú povrchu pôdy a prekážkam, čím zabraňujú poškodeniu pracovného zariadenia a zabezpečujú rovnomerný kontakt s pôdou. Časovanie a frekvencia orb medzi riadkami výrazne ovplyvňujú ich účinnosť, pričom väčšina plodín má prospech z viacerých prechodov počas raných fáz rastu.
Kritériá výberu pre optimálny výkon kultivátora
Zohľadnenie typu a stavu pôdy
Výber vhodných modelov kultivátorov vyžaduje starostlivé posúdenie charakteristík pôdy a typických pracovných podmienok, ktoré sa vyskytujú pri konkrétnych poľnohospodárskych operáciách. Ťažké ílovité pôdy si vyžadujú kultivátory s vyšším výkonom a robustnou konštrukciou, aby mohli preniknúť zhutnené vrstvy a dosiahnuť účinné premiešanie pôdy. Tieto podmienky uprednostňujú modely kultivátorov s ohnutými alebo skrútenými zubami, ktoré zabezpečujú agresívne zachytenie pôdy a zlepšenú činnosť premiešania. Naopak, piesočné pôdy vyžadujú jemnejšiu orbu, aby sa predišlo nadmernému narušeniu pôdy a zachovala sa jej štruktúra.
Obsah vlhkosti v pôde výrazne ovplyvňuje výkon a kritériá výberu kultivátora, pričom rôzne modely dosahujú optimálny výkon za odlišných podmienok vlhkosti. Na mokrej pôde sú potrebné kultivátory s výrazne rozmiestnenými čepeľami a agresívnym odstupom, aby sa zabránilo nánosom pôdy a ucpávaniu. Suché, tvrdé pôdy profitujú z kultivátorov s hrotitými čepeľami a vyšším výkonom, ktoré dokážu preniknúť odolnými povrchmi. Pochopenie typických vzorov vlhkosti pôdy počas vegetačného obdobia pomáha poľnohospodárom vybrať modely kultivátorov, ktoré spoľahlivo pracujú za miestnych podmienok.
Prítomnosť kameňov, pozostatkov po úrode a organickej hmoty ovplyvňuje požiadavky na trvanlivosť a prevádzkové aspekty ornej techniky. Polia s významným obsahom kameňov vyžadujú modely ornej techniky so systémami ochrany na pružinách alebo systémami automatického odpojenia, ktoré zabraňujú poškodeniu pri kontakte s podpovrchovými prekážkami. Podmienky s veľkým množstvom pozostatkov uprednostňujú orbely s dostatočnou voľnou výškou a schopnosťou manipulácie s pozostatkami, ktoré zabezpečujú hladký chod bez ucpávania alebo namotávania. Tieto environmentálne faktory priamo ovplyvňujú dlhodobú spoľahlivosť a požiadavky na údržbu rôznych modelov ornej techniky.
Prevádzkový rozsah a požiadavky na efektivitu
Rozsah pěstitelských operácií zásadným spôsobom určuje vhodnú veľkosť a kapacitu modelov kultivátorov potrebných na efektívne dokončenie sezónnej poľnej práce. Malé prevádzky s výmerou menej ako 10 árov môžu účinne využívať kompaktné modely kultivátorov, ktoré sa ovládajú pešo a ponúkajú flexibilitu a nízke prevádzkové náklady. Stredné prevádzky rozprestierajúce sa na ploche 10–100 árov zvyčajne profitujú zo strednej triedy samojazdných kultivátorov alebo malých kultivátorov na traktoroch, ktoré ponúkajú rovnováhu medzi produktivitou a obratnosťou.
Veľké komerčné prevádzky nad 100 árov vyžadujú modely kultivátorov s vysokou kapacitou, ktoré maximalizujú dennú produktivitu a minimalizujú čas potrebný na dokončenie práce na poli. Tieto prevádzky často odôvodňujú investíciu do širokých pracovných zariadení a pokročilých technologických funkcií, ktoré znižujú únavu obsluhy a zvyšujú presnosť orby. Vzťah medzi kapacitou zariadenia a dostupným časom práce počas optimálnych okien pre jaranie určuje minimálne požiadavky na produktivitu pre rôzne veľkosti poľnohospodárstva.
Dostupnosť pracovnej sily a úroveň zručností operátorov ovplyvňujú výber modelov kultivátorov s príslušnou zložitosťou a funkciami automatizácie. Prevádzky s obmedzenou dostupnosťou kvalifikovanej pracovnej sily profitujú z modelov kultivátorov so zjednodušeným ovládaním a minimálnymi požiadavkami na údržbu. Naopak, prevádzky s skúsenými operátormi môžu využívať sofistikovanejšie modely kultivátorov, ktoré ponúkajú rozšírené možnosti a výhody produktivity prostredníctvom pokročilých funkcií a presných ovládacích systémov.
Často kladené otázky
Aké faktory určujú najvhodnejší model kultivátora pre moju poľnohospodársku prevádzku
Výber optimálnych modelov kultivátorov závisí od niekoľkých kľúčových faktorov, vrátane veľkosti poľa, typu pôdy, požiadaviek na plodiny a prevádzkového rozpočtu. Menšie prevádzky pod 10 akrami zvyčajne profitujú z ručne vedených alebo kompaktných samojazdných kultivátorov, zatiaľ čo väčšie farmy vyžadujú kultivačné náradie pripevnené na traktor pre efektívne pokrytie plochy. Pôdne podmienky, ako obsah hliny, prítomnosť kamienkov a bežná vlhkosť, ovplyvňujú potrebný výkon a konštrukčné vlastnosti pre účinné kultivovanie. Zohľadnite svoje konkrétne plodiny, požiadavky na termíny kultivácie a dostupnú pracovnú silu pri hodnotení rôznych modelov kultivátorov, aby ste zabezpečili, že vybrané zariadenie spĺňa vaše prevádzkové potreby a ciele produktivity.
Ako udržiavam optimálny výkon kultivátora počas celej vegetačnej sezóny
Pravidelná údržba zabezpečuje konzistentný výkon a predlžuje životnosť kultivátorov počas náročného sezónneho používania. Skontrolujte a nabrúste hrable pred každým použitím, pričom udržiavajte správnu geometriu hrotov pre efektívne pronikanie do pôdy a odstraňovanie plevelu. Sledujte hladinu oleja v motore a vymeňte ho podľa odporúčaní výrobcu, zvyčajne každých 25–50 prevádzkových hodín. Udržiavajte čističe vzduchu v čistotom stave a každoročne vymeňte palivové filtre, aby ste zachovali výkon motora. Skontrolujte hnacie remene, reťaze a prevodovky na opotrebenie a správne mazanie. Kultivátory skladujte v suchých podmienkach počas mimo sezóny a vykonajte dôkladnú kontrolu pred začiatkom sezóny, aby ste identifikovali potrebné opravy alebo výmeny pred kritickými obdobiami orby.
Aké bezpečnostné opatrenia by som mal dodržiavať pri prevádzke rôznych modelov kultivátorov
Bezpečnostné protokoly sa môžu líšiť podľa modelov kultivátorov, no zahŕňajú niekoľko všeobecných opatrení pre všetkých operátorov. Vždy nosite primerané ochranné vybavenie vrátane ochranných okuliarov, ochrany sluchu a uzavretých topánok s dobrým priehľadom. Pred zahájaním kultivácie skontrolujte pracovnú plochu na prekážky, zavlažovacie potrubia a nebezpečenstvá nad úrovňou terénu. Nikdy sa nepokúšajte odstraňovať nečistoty alebo upravovať komponenty, keď motor beží alebo keď sú hrebeňe zapnuté. Pri prevádzke kultivátorov, ktoré sa ovládajú za chôdze, zachovávajte správne držanie tela a pevný postoj, aby ste predišli strate kontroly. U kultivátorov namontovaných na traktor sa uistite, že je správne pripevnená spojka a hydraulické pripojenia, než začnete s prevádzkou. Dodržiavajte pokyny výrobcu týkajúce sa bezpečných prevádzkových rýchlostí a vyhýbajte sa kultivácii na prudkých svahoch alebo vo vlhkých podmienkach, ktoré by mohli spôsobiť stratu trakcie alebo kontroly.
Ako určím správnu hĺbku kultivácie pre rôzne plodiny a pôdne podmienky
Správna hĺbka orania sa líši v závislosti od druhu plodiny, fázy rastu, pôdnych podmienok a cieľov orania. Vo všeobecnosti je pre už zavedené plodiny najvhodnejšia plytká orba do hĺbky 2,5 – 7,5 cm, čo zabraňuje poškodeniu koreňov pri súčasnom kontrolovaní burín a zachovaní vlhkosti pôdy. Hlbšia orba do hĺbky 10 – 20 cm je vhodná na počiatočnú prípravu pôdy a zaoranie organickej hmoty alebo pozostatkov plodín. Piesočnaté pôdy vyžadujú plytšiu orbu, aby nedošlo k nadmernému narušeniu pôdy, zatiaľ čo ťažšie ílové pôdy môžu profitovať z hlbšej orby na rozbitie zhutnených vrstiev. Sledujte stav pôdy a reakciu plodín, aby ste určili optimálnu hĺbku orby pre vaše konkrétne modely oracích strojov, a upravujte ju podľa sezónnych podmienok a cieľov orania.
Obsah
- Základné vlastnosti moderných modelov kultivátorov
- Kompaktné modely záhradných kultivátorov pre malé prevádzky
- Modely kultivátorov strednej triedy pre komerčné záhrady
- Modely kultivátorov pre rozsiahle poľnohospodárske pestovanie
- Kritériá výberu pre optimálny výkon kultivátora
-
Často kladené otázky
- Aké faktory určujú najvhodnejší model kultivátora pre moju poľnohospodársku prevádzku
- Ako udržiavam optimálny výkon kultivátora počas celej vegetačnej sezóny
- Aké bezpečnostné opatrenia by som mal dodržiavať pri prevádzke rôznych modelov kultivátorov
- Ako určím správnu hĺbku kultivácie pre rôzne plodiny a pôdne podmienky