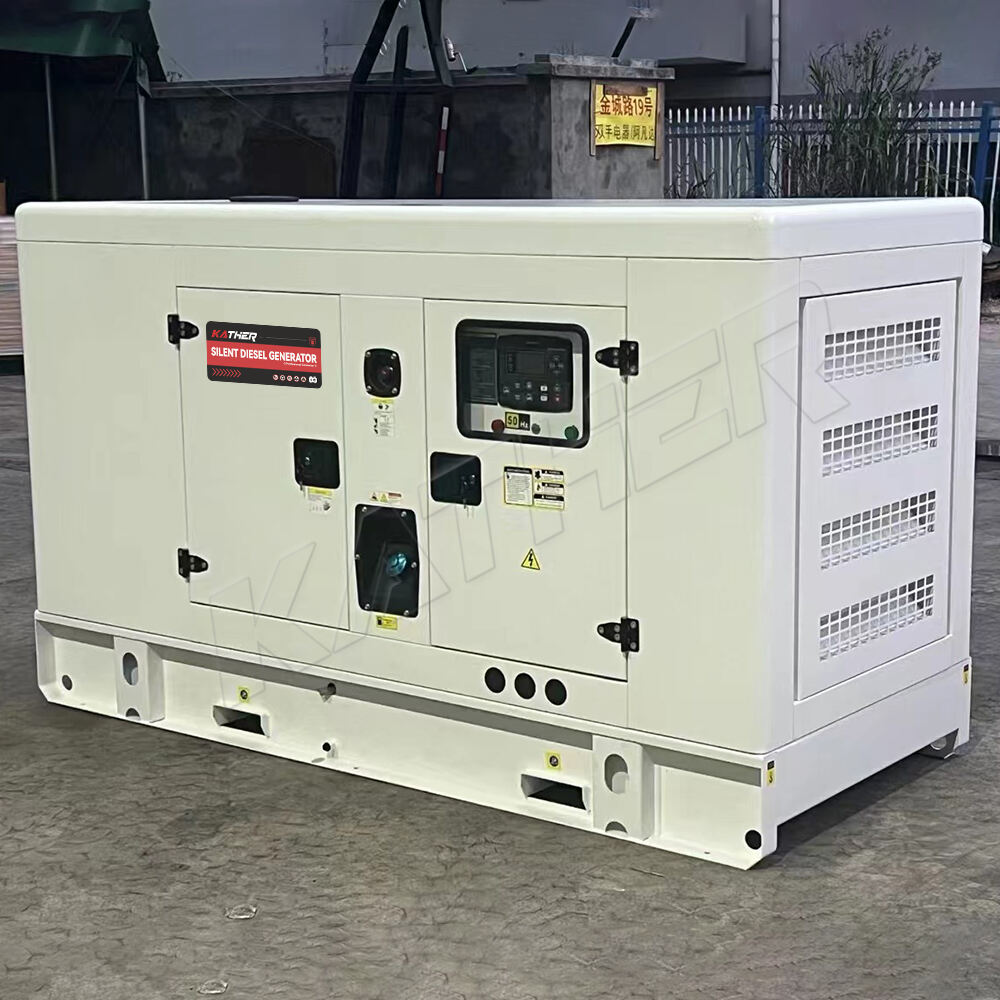
Διαστασιολόγηση Αθόρυβων Συγκροτημάτων Πετρελαιομηχανών για Απομακρυσμένες Κατασκευαστικές Εγκαταστάσεις
Οι απομακρυσμένες δομικές προκλήσεις φέρνουν μοναδικές προκλήσεις που απαιτούν αξιόπιστες λύσεις παροχής ηλεκτρικής ενέργειας. Σε αντίθεση με τις αστικές περιοχές εργασίας, όπου συνήθως μπορεί να χρησιμοποιηθεί το υπάρχον ηλεκτρικό δίκτυο, οι απομακρυσμένες περιοχές δεν διαθέτουν συχνά τέτοια υποδομή. Η απουσία σταθερής παροχής ηλεκτρικής ενέργειας σημαίνει ότι οι εργολάβοι πρέπει να βασίζονται σε ανεξάρτητες πηγές ενέργειας για να συνεχίζεται το έργο. Σε αυτά τα σενάρια, το Γεννήτρια ντίζελ έχει γίνει η προτιμώμενη επιλογή. Ήσυχη στη λειτουργία της, αλλά ισχυρή στην απόδοση, αυτή η κατηγορία γεννήτριας εξασφαλίζει αδιάλειπτη παραγωγικότητα, ενώ ελαχιστοποιεί τη διαταραχή του εργασιακού περιβάλλοντος.
Η σωστή διαστασιολόγηση ενός Γεννήτρια ντίζελ είναι απαραίτητη. Η επιλογή ενός συνόλου που είναι πολύ μικρό οδηγεί σε υπερφόρτωση, διακοπές λειτουργίας και βλάβες εξοπλισμού, ενώ η υπερδιάσταση αυξάνει το κόστος και σπαταλά καύσιμο. Το άρθρο αυτό εξετάζει τη διαδικασία διαστασιοποίησης ήσυχων ηλεκτροπαραγωγών ζευγών Diesel για απομακρυσμένες κατασκευαστικές θέσεις, εξερευνώντας παράγοντες όπως οι απαιτήσεις φορτίου, οι περιβαλλοντικοί παράγοντες, οι περιοριστικές συνθήκες θορύβου και η μακροχρόνια αποτελεσματικότητα.
Γιατί οι Ήσυχοι Ηλεκτροπαραγωγές Ζεύξεις Diesel είναι Απαραίτητες για Απομακρυσμένες Κατασκευές
Οι κατασκευαστικές θέσεις είναι εξ ορισμού θορυβώδεις, με βαρύ εξοπλισμό, τρυπήματα και εκσκαφές να λαμβάνουν χώρα καθ' όλη τη διάρκεια της ημέρας. Η προσθήκη μιας υπερβολικά θορυβώδους ηλεκτροπαραγωγού ζεύξης στο σύνολο της κατασκευής δεν προκαλεί μόνο διαταραχές στην επικοινωνία των εργαζομένων, αλλά επίσης κινδυνεύει να παραβεί τους τοπικούς περιορισμούς θορύβου. Μια ήσυχη ηλεκτροπαραγωγός ζεύξη Diesel έχει σχεδιαστεί ειδικά με ακουστικούς θαλάμους και σιγαστήρες που μειώνουν τον θόρυβο λειτουργίας, παρέχοντας παράλληλα επαρκή ηλεκτρική ενέργεια. Αυτό επιτρέπει στους εργολήπτες να καλύπτουν τις ενεργειακές ανάγκες χωρίς να θέτουν σε κίνδυνο την ασφάλεια και την άνεση.
Εκτός από τον έλεγχο της ηχορύπανσης, η αξιοπιστία των Πετρελαιοκινητήρων τους καθιστά ιδιαίτερα κατάλληλους για απαιτητικά περιβάλλοντα. Είναι αρκετά ανθεκτικοί ώστε να αντέχουν σε δύσκολες καιρικές συνθήκες, μεταβαλλόμενα φορτία και μεγάλες ώρες λειτουργίας. Επιπλέον, το πετρέλαιο είναι εύκολα διαθέσιμο και μπορεί να αποθηκευτεί για μεγάλα χρονικά διαστήματα, καθιστώντας το πρακτική επιλογή για έργα που λειτουργούν μακριά από δίκτυα διανομής καυσίμων.
Αξιολόγηση Απαιτήσεων Ισχύος
Το πρώτο βήμα στη διαστασιολόγηση ενός Πετρελαιοκινητήρα είναι να αξιολογηθεί η συνολική απαίτηση ισχύος της κατασκευαστικής περιοχής. Αυτό περιλαμβάνει την καταγραφή κάθε συσκευής που θα καταναλώνει ενέργεια, από βαριά μηχανήματα όπως γερανοί και αναμεικτήρες μέχρι συστήματα φωτισμού, εργασιακές καμπίνες, εξοπλισμό επικοινωνίας και συσκευές ασφαλείας. Κάθε αντικείμενο πρέπει να κατηγοριοποιηθεί με βάση το αν απαιτεί συνεχή παροχή ισχύος, ενδιάμεση παροχή ή μέγιστη ισχύ κατά την εκκίνηση.
Συνεχείς φορτία περιλαμβάνουν συστήματα όπως ο φωτισμός, το HVAC και οι αντλίες νερού που πρέπει να λειτουργούν συνεχώς καθ' όλη τη διάρκεια της ημέρας. Ενδιάμεσα φορτία περιλαμβάνουν μηχανήματα συγκόλλησης, ηλεκτρικά εργαλεία και συμπιεστές που μπορεί να χρησιμοποιούνται μόνο κατά τη διάρκεια ορισμένων εργασιών. Τα φορτία εκκίνησης, ιδιαίτερα για ηλεκτροκινητήρες και συμπιεστές, μπορούν να καταναλώνουν δύο έως τρεις φορές την κανονική λειτουργική ισχύ κατά τα πρώτα δευτερόλεπτα. Ένας Διανομέας Πετρελαίου πρέπει να έχει διαστασιολογηθεί ώστε να αντέχει αυτές τις διακυμάνσεις χωρίς να προκαλεί διακοπές ή επιβλαβείς πτώσεις τάσης.
Προσθέτοντας με προσοχή το συνολικό αριθμό κιλοβάτ που απαιτούνται για συνεχή χρήση, λαμβάνοντας υπόψη την ποικιλία της χρήσης και προσθέτοντας χωρητικότητα για την κορυφαία ζήτηση, οι εργολάβοι μπορούν να εκτιμήσουν την απαιτούμενη ισχύ του γεννήτριας.
Περιβαλλοντικές και Συνθήκες Χώρου
Σε απομακρυσμένες τοποθεσίες συχνά παρουσιάζονται ακραίες περιβαλλοντικές συνθήκες που επηρεάζουν άμεσα την απόδοση της γεννήτριας. Το υψηλό υψόμετρο μειώνει την πυκνότητα του αέρα, με αποτέλεσμα τη μείωση της αποδοτικότητας της καύσης στη μηχανή. Ως εκ τούτου, η ισχύς θα πρέπει να μειώνεται κατά περίπου τρία έως τέσσερα τοις εκατό για κάθε 300 μέτρα πάνω από τα 1000 μέτρα υψόμετρο. Επίσης, οι υψηλές θερμοκρασίες περιβάλλοντος μειώνουν την αποδοτικότητα, ενώ σε σκονιστά περιβάλλοντα απαιτούνται ενισχυμένα συστήματα φιλτραρίσματος για να αποφεύγεται η φθορά της μηχανής.
Για παράδειγμα, μια ηλεκτροπαραγωγή μονάδα ντίζελ με ονομαστική ισχύ 200 kVA στην επιφάνεια της θάλασσας μπορεί να παρέχει μόνο 170 έως 180 kVA σε ορεινό περιβάλλον στα 2000 μέτρα υψόμετρο. Η μη λήψη υπόψη αυτών των παραγόντων μείωσης της απόδοσης οδηγεί συχνά σε μειωμένη απόδοση και πρόωρη φθορά.
Διαφοροποίηση φορτίου και μελλοντική ανάπτυξη
Τα κατασκευαστικά έργα εξελίσσονται. Στην αρχή, μπορεί να απαιτούνται μόνο λίγα εργαλεία, όμως καθώς προχωρά το έργο, προστίθενται περισσότερες καμπίνες, γερανοί και εξοπλισμός ολοκλήρωσης. Ένας γεννήτρια πετρελαίου που έχει επιλεγεί μόνο για τις αρχικές ανάγκες σύντομα γίνεται ανεπαρκής. Είναι συνεπώς σκόπιμο να επιλέγεται η ισχύς της γεννήτριας πετρελαίου έχοντας υπόψη τη μελλοντική ανάπτυξη, προσθέτοντας συχνά δέκα έως είκοσι τοις εκατό χωρητικότητα πέραν των άμεσων αναγκών.
Αυτό το επιπλέον περιθώριο εξασφαλίζει ότι η γεννήτρια παραμένει επαρκής σε όλη τη διάρκεια του έργου, αποτρέποντας ακριβές αντικαταστάσεις ή παράλληλες εγκαταστάσεις αργότερα.
Ώρες λειτουργίας και κατανάλωση καυσίμου
Σε απομακρυσμένες τοποθεσίες μπορεί να απαιτείται οι γεννήτριες πετρελαίου να λειτουργούν για παρατεταμένες ώρες, μερικές φορές είκοσι τέσσερις ώρες την ημέρα. Η κατανάλωση καυσίμου γίνεται έτσι κρίσιμος παράγοντας τόσο για το λειτουργικό κόστος όσο και για τη διακίνηση. Οι υπερδιαστασιοποιημένες γεννήτριες που λειτουργούν με χαμηλά φορτία καταναλώνουν περισσότερο καύσιμο ανά χιλιοβάτ ώρα παραγόμενης ενέργειας, ενώ οι υποδιαστασιοποιημένες μονάδες λειτουργούν συνεχώς με πλήρες φορτίο και υφίστανται φθορά.
Για βέλτιστη απόδοση, ένας πετρελαιοκινητήρας θα πρέπει συνήθως να λειτουργεί στο εύρος του 60% έως 80% της ονομαστικής του ισχύος. Αυτό εξασφαλίζει μειωμένη κατανάλωση καυσίμου ανά μονάδα ενέργειας και παρατείνει τη διάρκεια ζωής του κινητήρα. Οι εργολήπτες θα πρέπει να εξισορροπούν την ισχύ της γεννήτριας με το αναμενόμενο φορτίο, ώστε να διατηρείται αυτό το βέλτιστο εύρος λειτουργίας.
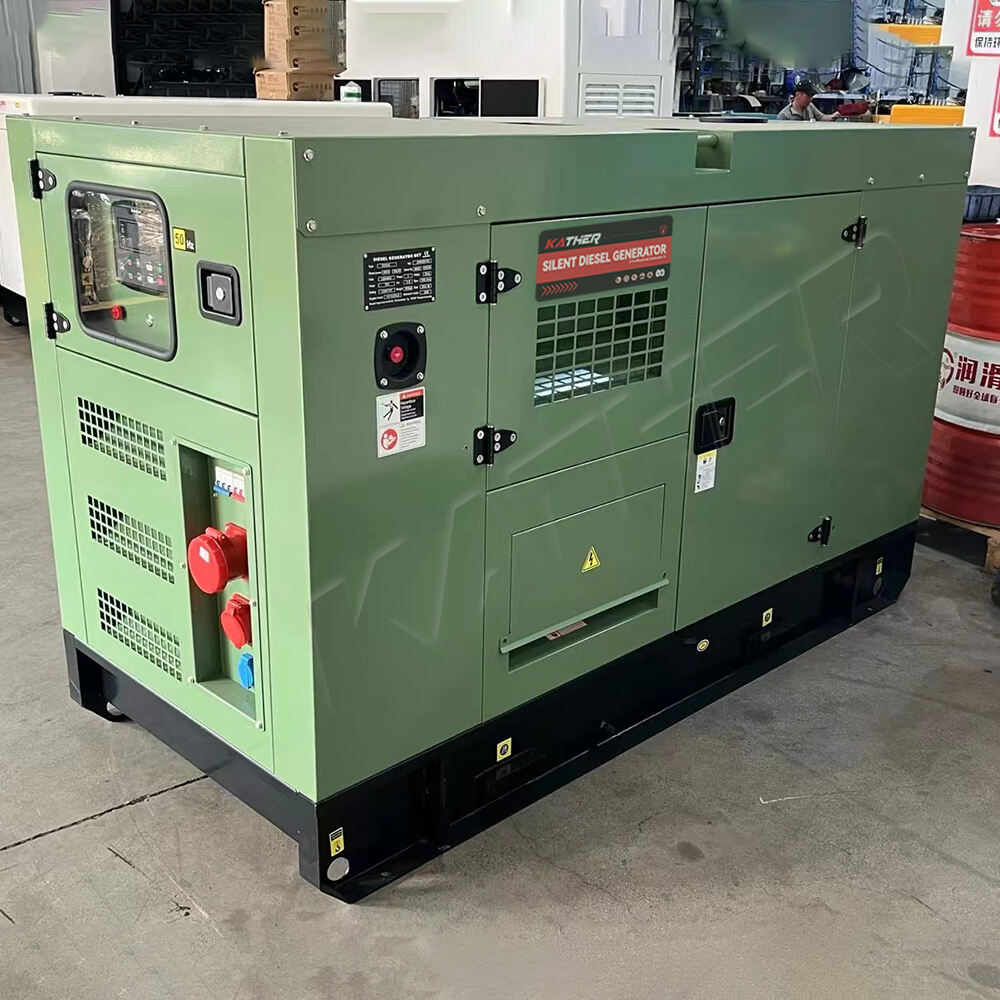

Ποιότητα και Σταθερότητα Ρεύματος
Όλα τα φορτία δεν είναι τα ίδια. Ενώ πολλά εργαλεία κατασκευής ανέχονται τις διακυμάνσεις τάσης, ευαίσθητα ηλεκτρονικά όπως οι υπολογιστές, οι συσκευές δικτύου και τα συστήματα εποπτείας ασφαλείας απαιτούν σταθερή τάση και συχνότητα. Για τον λόγο αυτό, ένας πετρελαιοκινητήρας θα πρέπει να είναι εξοπλισμένος με προηγμένους αυτόματους ρυθμιστές τάσης και συστήματα ελέγχου συχνότητας. Η λανθασμένη επιλογή μεγέθους μπορεί να προκαλέσει πτώσεις τάσης, ιδιαίτερα κατά την εκκίνηση των κινητήρων, με αποτέλεσμα βλάβες ή δυσλειτουργίες.
Βήματα για τη σωστή επιλογή μεγέθους ησυχόφωνου πετρελαιοκινητήρα
Υπολογισμός της συνολικής ζήτησης
Η διαδικασία ξεκινά με τη σύνταξη ενός λεπτομερούς καταλόγου φορτίων. Κάθε στοιχείο καταγράφεται με την κατανάλωσή του σε κιλοβάτ, τον συντελεστή ισχύος του και τα χαρακτηριστικά εκκίνησής του. Διαχωρίζοντας τα φορτία σε κατηγορίες – συνεχή, ενδιάμεσα και ορμητικά – ο εργολήπτης μπορεί να υπολογίσει τη μέγιστη ταυτόχρονη ζήτηση. Συνήθως προστίθεται ένα περιθώριο ασφαλείας δέκα έως δεκαπέντε τοις εκατό.
Προσδιορισμός Απαιτήσεων Φάσης
Ορισμένος εξοπλισμός απαιτεί τριφασική παροχή ρεύματος, ενώ μικρότερα εργαλεία μπορεί να χρειάζονται μόνο μονοφασική. Τα εργοτάξια συνήθως απαιτούν έναν τριφασικό Πετρελαιοκινητήρα για να εξασφαλιστεί η συμβατότητα με τις βαριές μηχανές. Ο έγκαιρος προσδιορισμός των απαιτήσεων φάσης αποτρέπει την ασυμβατότητα, η οποία μπορεί να προκαλέσει αναποτελεσματικότητα ή βλάβη στον εξοπλισμό.
Εφαρμογή Συντελεστών Μείωσης
Οι περιβαλλοντικές συνθήκες, όπως η θερμοκρασία, το υψόμετρο και η σκόνη, πρέπει να ληφθούν υπόψη κατά την αξιολόγηση της ισχύος της γεννήτριας. Οι κατασκευαστές παρέχουν πίνακες μείωσης ισχύος που βοηθούν στην προσαρμογή της ονομαστικής ισχύος στην πραγματική απόδοση. Αυτό το βήμα εξασφαλίζει ότι η επιλεγμένη γεννήτρια θα μπορεί να παρέχει αξιόπιστη ισχύ ακόμη και σε δυσμενείς συνθήκες.
Ταίριασμα Προφίλ Φορτίου
Η Πετρελαιομηχανή Παραγωγής Ηλεκτρικής Ενέργειας πρέπει να ανταποκρίνεται στο αναμενόμενο ημερήσιο προφίλ φορτίου, λειτουργώντας αποδοτικά το μεγαλύτερο μέρος της ημέρας και ανταποκρινόμενη στις περιστασιακές κορυφές. Η συνεχής λειτουργία στο εύρος φορτίου εξήντα έως ογδόντα τοις εκατό ελαχιστοποιεί τη συντήρηση, την κατανάλωση καυσίμου και τις διακοπές λειτουργίας.
Σχεδιασμός για μελλοντικές ανάγκες
Καθώς εξελίσσεται το έργο, είναι σχεδόν βέβαιο ότι θα προκύψουν επιπλέον απαιτήσεις ισχύος. Ενσωματώνοντας ένα περιθώριο στους υπολογισμούς μέγεθος, οι εργολήπτες αποφεύγουν την έλλειψη χωρητικότητας. Αυτή η προνοητικότητα εξοικονομεί χρήματα και αποφεύγει περιττές διακοπές στη λειτουργία.
Η Σημασία του Ελέγχου της Θορύβου
Οι ηχητικά μονωμένοι πετρελαιοκινητήρες επιτυγχάνουν μειωμένα επίπεδα θορύβου μέσω προσεκτικά σχεδιασμένων ακουστικών περιβλημάτων και σιγαστήρων. Σε απομακρυσμένες δομικές περιοχές, αυτό είναι σημαντικό όχι μόνο για την άνεση των εργαζομένων, αλλά και για την τήρηση περιβαλλοντικών προδιαγραφών. Πολλές περιοχές επιβάλλουν αυστηρά όρια θορύβου, ακόμη και σε μη κατοικημένες ζώνες. Η επιλογή ενός πετρελαιοκινητήρα με αποδεδειγμένη ακουστική απόδοση εξασφαλίζει ομαλότερη λειτουργία και λιγότερες διαμάχες με τις γειτονικές κοινότητες.
Η μείωση του θορύβου συμβάλλει επίσης στην ασφάλεια. Οι εργαζόμενοι πρέπει να μπορούν να ακούν συναγερμούς, σήματα και ο ένας τον άλλον. Ο υπερβολικός θόρυβος οδηγεί σε παρεξηγήσεις και αυξάνει τον κίνδυνο ατυχημάτων. Ένας ηχητικά μονωμένος πετρελαιοκινητήρας προστατεύει επομένως τόσο την τήρηση των κανονισμών όσο και την ασφάλεια στον χώρο εργασίας.
Διαχείριση Καυσίμων και Αυτονομία
Μία από τις μεγαλύτερες προκλήσεις στην απομακρυσμένη κατασκευή είναι η εφοδιαστική αλυσίδα καυσίμων. Οι παραδόσεις μπορεί να είναι σπάνιες λόγω κακών οδών ή καιρικών συνθηκών, γι' αυτό τους σταθμούς παραγωγής ηλεκτρικής ενέργειας πετρελαίου θα πρέπει να τους επιλέγετε ώστε να έχουν αυτονομία. Μεγάλες δεξαμενές βάσης ή εξωτερικές δεξαμενές παρέχουν είκοσι τέσσερις έως σαράντα οκτώ ώρες λειτουργίας με μέση φόρτιση. Προσεκτικός σχεδιασμός καυσίμων εξασφαλίζει ότι οι εργασίες δεν θα σταματήσουν απρόσμενα.
Οι υβριδικές λύσεις που συνδυάζουν σταθμούς παραγωγής ηλεκτρικής ενέργειας πετρελαίου με μπαταρίες αποθήκευσης ή ηλιακά πάνελ γίνονται δημοφιλείς, μειώνοντας την εξάρτηση από καύσιμα και παρέχοντας πιο ομαλή διαχείριση φορτίου. Αυτά τα συστήματα επεκτείνουν τα διαστήματα αναπλήρωσης καυσίμου ενώ διατηρούν τη συνεχή παροχή ηλεκτρικής ενέργειας.
Σχετικά με τη συντήρηση
Η σωστή επιλογή σταθμού παραγωγής ηλεκτρικής ενέργειας πετρελαίου δεν έχει να κάνει μόνο με την ταίριασμα της χωρητικότητας, αλλά και με τη διασφάλιση της δυνατότητας συντήρησης. Οι σταθμοί παραγωγής ηλεκτρικής ενέργειας πετρελαίου που λειτουργούν σε απομακρυσμένες περιοχές χρειάζονται απλοποιημένες επιλογές συντήρησης, εύκολη πρόσβαση στα φίλτρα και αξιόπιστα συστήματα παρακολούθησης. Η επιλογή ενός σταθμού παραγωγής ηλεκτρικής ενέργειας πετρελαίου που είναι ελαφρώς μεγαλύτερος από τις ελάχιστες απαιτήσεις μειώνει την καταπόνηση και επεκτείνει τα διαστήματα συντήρησης.
Οι τεχνολογίες προγνωστικής συντήρησης, όπως οι αισθητήρες απομακρυσμένης παρακολούθησης, βοηθούν επίσης τους εργολήπτες να εντοπίζουν προβλήματα πριν συμβούν βλάβες. Αυτό είναι ιδιαίτερα χρήσιμο σε απομακρυσμένες τοποθεσίες, όπου η διακοπή λειτουργίας μπορεί να είναι εξαιρετικά δαπανηρή.
Συνηθισμένα λάθη στον υπολογισμό της διάστασης
Ένα από τα πιο συνηθισμένα λάθη είναι η υπερδιάσταση ενός Πετρελαιοκινητήρα για λόγους ασφάλειας. Ενώ αυτό μπορεί να φαίνεται προνοητικό, το αποτέλεσμα είναι μη αποτελεσματική λειτουργία, συσσώρευση υγρασίας, σχηματισμός άνθρακα και περιττές δαπάνες καυσίμου. Αντίθετα, η υποδιάσταση οδηγεί σε συνεχείς υπερφορτώσεις, υψηλή φθορά και συχνές βλάβες.
Ένα άλλο λάθος είναι η παράλειψη των ριπών έναρξης των ηλεκτροκινητήρων. Χωρίς να ληφθούν υπόψη αυτές οι κορυφές, ο πετρελαιοκινητήρας μπορεί να διακόψει τη λειτουργία του ή να προκαλέσει πτώση τάσης με ζημιές. Με παρόμοιο τρόπο, η μη εφαρμογή συντελεστών διόρθωσης για υψόμετρο και θερμοκρασία έχει ως αποτέλεσμα απόδοση που δεν καλύπτει τις ανάγκες του έργου.
Μέλλον Πετρελαιοκινητήρων σε Απομακρυσμένες Κατασκευές
Παρότι οι ανανεώσιμες πηγές ενέργειας κερδίζουν έδαφος, οι Διανομείς Πετρελαίου παραμένουν απαραίτητοι για απομακρυσμένες κατασκευές. Τα μελλοντικά μοντέλα αναμένεται να ενσωματώσουν έξυπνη παρακολούθηση, συμβατότητα με υβριδικά συστήματα και βελτιωμένη απόδοση εκπομπών. Οι Αθόρυβοι Διανομείς Πετρελαίου θα συνεχίσουν να εξελίσσονται, προσφέροντας ακόμη χαμηλότερα επίπεδα θορύβου και υψηλότερη καυσίμου απόδοση. Αυτές οι εξελίξεις θα τους κάνουν πιο φιλικούς προς το περιβάλλον, ενώ θα διατηρούν την ανθεκτικότητα στην οποία οι εργολήπτες βασίζονται.
Συμπέρασμα
Οι Αθόρυβοι Διανομείς Πετρελαίου δεν είναι απλώς προσωρινές λύσεις ηλεκτροδότησης, είναι κρίσιμοι συντελεστές για την υλοποίηση απομακρυσμένων κατασκευαστικών έργων. Η σωστή διαστασιολόγηση εξασφαλίζει ότι κάθε συσκευή, από βαριά μηχανήματα μέχρι συστήματα ασφαλείας, θα λειτουργεί χωρίς διακοπές. Μέσα από προσεκτική ανάλυση των απαιτήσεων φορτίου, λαμβάνοντας υπόψη τις περιβαλλοντικές συνθήκες και σχεδιάζοντας για μελλοντικές ανάγκες, οι εργολήπτες μπορούν να επιλέξουν Διανομέα Πετρελαίου που θα ισορροπεί αποδοτικότητα, ανθεκτικότητα και κόστος.
Τα πλεονεκτήματα ξεπερνούν την αξιόπιστη παροχή ενέργειας. Ένας γεννήτριας κατάλληλου μεγέθους μειώνει την κατανάλωση καυσίμου, ελαχιστοποιεί τη συντήρηση και εξασφαλίζει την τήρηση των κανονισμών περί θορύβου. Για απομακρυσμένες δομικές περιοχές, όπου οι καθυστερήσεις είναι δαπανηρές και η πρόσβαση περιορισμένη, η επένδυση χρόνου για τη σωστή επιλογή μιας ηχομονωτικής πετρελαιογεννήτριας είναι μία από τις πιο σοφές αποφάσεις που μπορούν να πάρουν οι υπεύθυνοι έργων.
Συχνές Ερωτήσεις
Πώς μπορώ να ξέρω τι μέγεθος πετρελαιογεννήτριας χρειάζεται η κατασκευαστική μου περιοχή;
Πρέπει να υπολογίσετε το συνολικό φορτίο, να λάβετε υπόψη τις διακυμάνσεις εκκίνησης, να εφαρμόσετε παράγοντες μείωσης λόγω περιβαλλοντικών συνθηκών και να προσθέσετε ένα περιθώριο για μελλοντική ανάπτυξη.
Μπορεί μια πετρελαιογεννήτρια να λειτουργεί συνεχώς σε απομακρυσμένη περιοχή;
Ναι. Οι σύγχρονες πετρελαιογεννήτριες έχουν σχεδιαστεί να λειτουργούν για μεγάλες ώρες, με την προϋπόθεση ότι έχουν επιλεγεί σωστά ως προς το μέγεθος και ότι συντηρούνται τακτικά.
Γιατί το μεγαλύτερο μέγεθος μιας πετρελαιογεννήτριας είναι πρόβλημα;
Η υπερδιάσταση οδηγεί σε αναποτελεσματική κατανάλωση καυσίμου, σε λειτουργία με χαμηλό φορτίο και σε ζημιές στον κινητήρα από υγρή επισσαυροποίηση και εναπόθεση άνθρακα.
Πόσο συχνά πρέπει να γίνεται συντήρηση στις πετρελαιογεννήτριες σε κατασκευαστικές περιοχές;
Πρέπει να γίνονται τακτικοί έλεγχοι καθημερινά, με συντήρηση λαδιού, φίλτρου και ψυκτικού βάσει των ωρών λειτουργίας και των συστάσεων του κατασκευαστή.
Είναι οι υβριδικές λύσεις καλύτερες από τις Διανομείς Πετρελαίου;
Τα υβριδικά συστήματα μπορούν να μειώσουν την κατανάλωση καυσίμου και τις εκπομπές, ωστόσο οι Διανομείς Πετρελαίου παραμένουν απαραίτητες ως αξιόπιστη βάση για απομακρυσμένα δομικά έργα.
Πίνακας Περιεχομένων
- Γιατί οι Ήσυχοι Ηλεκτροπαραγωγές Ζεύξεις Diesel είναι Απαραίτητες για Απομακρυσμένες Κατασκευές
- Αξιολόγηση Απαιτήσεων Ισχύος
- Περιβαλλοντικές και Συνθήκες Χώρου
- Διαφοροποίηση φορτίου και μελλοντική ανάπτυξη
- Ώρες λειτουργίας και κατανάλωση καυσίμου
- Ποιότητα και Σταθερότητα Ρεύματος
- Βήματα για τη σωστή επιλογή μεγέθους ησυχόφωνου πετρελαιοκινητήρα
- Η Σημασία του Ελέγχου της Θορύβου
- Διαχείριση Καυσίμων και Αυτονομία
- Σχετικά με τη συντήρηση
- Συνηθισμένα λάθη στον υπολογισμό της διάστασης
- Μέλλον Πετρελαιοκινητήρων σε Απομακρυσμένες Κατασκευές
- Συμπέρασμα
-
Συχνές Ερωτήσεις
- Πώς μπορώ να ξέρω τι μέγεθος πετρελαιογεννήτριας χρειάζεται η κατασκευαστική μου περιοχή;
- Μπορεί μια πετρελαιογεννήτρια να λειτουργεί συνεχώς σε απομακρυσμένη περιοχή;
- Γιατί το μεγαλύτερο μέγεθος μιας πετρελαιογεννήτριας είναι πρόβλημα;
- Πόσο συχνά πρέπει να γίνεται συντήρηση στις πετρελαιογεννήτριες σε κατασκευαστικές περιοχές;
- Είναι οι υβριδικές λύσεις καλύτερες από τις Διανομείς Πετρελαίου;